Title: Leveraging Big Data for Poverty Alleviation: A Comprehensive Overview
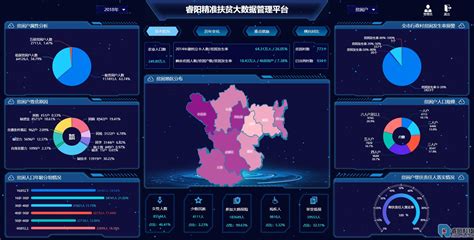
In recent years, the intersection of big data and poverty alleviation efforts has emerged as a promising avenue for driving social change and economic development. Through the utilization of advanced data analytics techniques, governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders can gain valuable insights into poverty dynamics, target interventions more effectively, and monitor progress towards sustainable development goals. Let's delve into the various aspects of how big data is being leveraged to empower disadvantaged communities and advance the cause of poverty reduction.
1. Datadriven Poverty Identification:
Big data analytics enables the identification and characterization of poverty at unprecedented granularity. By harnessing diverse data sources such as satellite imagery, mobile phone usage patterns, social media activity, and financial transactions, analysts can construct multidimensional poverty indices that capture not only income levels but also access to essential services, educational attainment, healthcare utilization, and other relevant indicators. This nuanced understanding of poverty facilitates the design of tailored interventions that address the specific needs of different population segments.
2. Precision Targeting of Interventions:
Traditional poverty alleviation programs often suffer from a lack of targeting precision, leading to inefficient resource allocation and limited impact. Big data analytics allows policymakers to target interventions with surgical precision, directing resources towards the individuals and communities most in need. Machine learning algorithms can identify predictive markers of poverty risk, enabling proactive intervention strategies that prevent vulnerable households from falling deeper into poverty traps.
3. Dynamic Monitoring and Evaluation:
Realtime data streams enable dynamic monitoring and evaluation of poverty alleviation initiatives, providing policymakers with timely feedback on program effectiveness and identifying areas for improvement. Through the integration of sensor networks, IoT devices, and geospatial data platforms, stakeholders can track changes in socioeconomic indicators, monitor the delivery of services, and assess the impact of interventions on the ground. This iterative feedback loop enables adaptive management practices that enhance the efficiency and efficacy of poverty reduction efforts over time.
4. Financial Inclusion and Digital Payments:
Access to financial services is a critical driver of economic empowerment and poverty reduction. Big data technologies are facilitating the expansion of financial inclusion initiatives, particularly in underserved rural and remote areas. Mobile money platforms, digital payment systems, and blockchainbased solutions are enabling lowcost, secure, and convenient financial transactions, empowering individuals to save, borrow, and invest in productive assets. By leveraging transactional data, financial institutions can extend credit to unbanked populations and tailor financial products to their specific needs, fostering entrepreneurship and income generation opportunities.
5. Predictive Analytics for Risk Mitigation:
Big data analytics can play a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with natural disasters, climate change, and other external shocks that disproportionately affect disadvantaged communities. By analyzing historical data on weather patterns, geological hazards, and socioeconomic vulnerabilities, predictive models can anticipate emerging threats and inform proactive risk management strategies. Early warning systems, coupled with targeted evacuation plans and contingency measures, can help minimize the human and economic toll of disasters and build resilience in vulnerable populations.
6. Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
While big data holds immense potential for poverty alleviation, it also raises important ethical and privacy considerations that must be addressed. Data collection, storage, and usage practices must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to ensure the protection of individual rights and prevent potential abuses. Transparency, informed consent, data anonymization, and robust cybersecurity measures are essential components of responsible data stewardship. Moreover, efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide and ensure equitable access to the benefits of datadriven development, particularly among marginalized communities.
In conclusion, the integration of big data analytics into poverty alleviation strategies offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance the effectiveness, efficiency, and equity of development interventions. By harnessing the power of data, stakeholders can gain deeper insights into poverty dynamics, target interventions more precisely, and monitor progress towards sustainable development goals in realtime. However, it is essential to navigate the ethical and privacy challenges inherent in big data initiatives and ensure that the benefits accrue to those who need them most. Only through concerted action and responsible innovation can we harness the full potential of big data to create a more inclusive and prosperous society for all.
标签: 大数据 扶贫 惠民扶贫资金大数据监察平台 惠民大数据扶贫信息平台 扶贫惠农资金大数据平台


评论列表
扶贫惠农资金大数据平台:精准助力,普降福泽,全域赋能农业发展